EQUIPMENT AND DATASETS - SANTORINI SUMMER SCHOOL
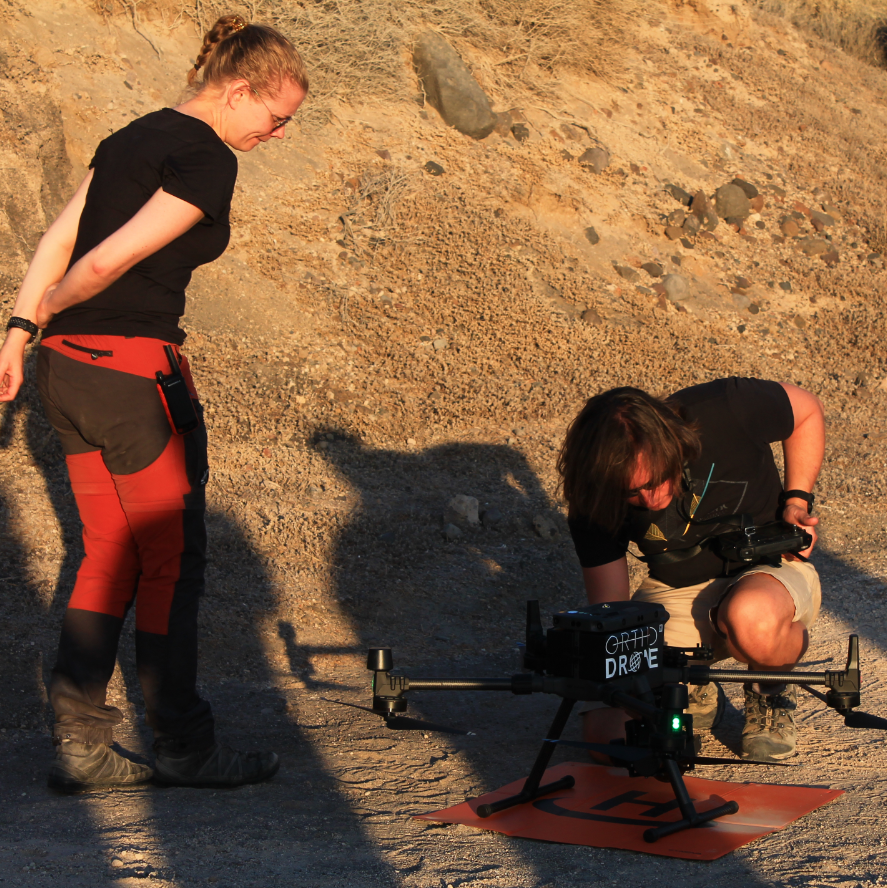
UNCREWED AERIAL VEHICLES
Uncrewed Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, are aircraft operated remotely without a pilot onboard. In coastal mapping, UAVs are equipped with advanced sensors and high-resolution cameras to capture detailed imagery and data of shorelines and coastal features. These aerial surveys provide precise, up-to-date insights into coastal erosion, habitat changes, and environmental dynamics. By offering efficient and accurate monitoring, UAVs play a crucial role in environmental management, disaster response, and scientific research, helping experts track and analyze coastal changes with unprecedented detail.
Several field activities during the school focused on UAV-based data collection, led by the UNIMIB and Orthodrone research teams at various locations around Santorini. Students gained hands-on experience in the entire workflow of UAV surveys, from planning and data acquisition to processing and analysis. During the laboratory session, they explored the fundamentals of data processing, using software like Agisoft Metashape and CloudCompare to visualize and analyze the collected data. This interactive approach allowed them to develop practical skills while experimenting with industry-standard tools.


GEOSLAM
GeoSLAM is a state-of-the-art handheld laser scanner equipped with a LiDAR sensor, designed for rapid and accurate 3D mapping. Utilizing Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) algorithms, it enables the acquisition of geo-referenced 3D point clouds, making it a powerful tool for a wide range of applications, including slope stability assessment, monitoring 3D geomorphic processes, forestry measurements, plant biomass estimation, urban planning, and underground mapping. This advanced system captures up to 300,000 points per second, with a maximum range of 100 meters and an accuracy of less than 3 cm. The output includes precisely aligned and colorized 3D point clouds, along with panoramic imagery sample points, offering detailed spatial information for analysis and visualization.
During the Santorini Summer School, the research teams conducted multiple GeoSLAM surveys, actively engaging all students in field data collection. The data acquired along Red Beach was later processed during a dedicated laboratory session, allowing participants to analyze and refine the 3D models. Additional datasets were collected at Vlychada Beach and the Metaxa Mine, further enhancing the scope of the study and providing valuable hands-on experience in geospatial data processing and analysis.
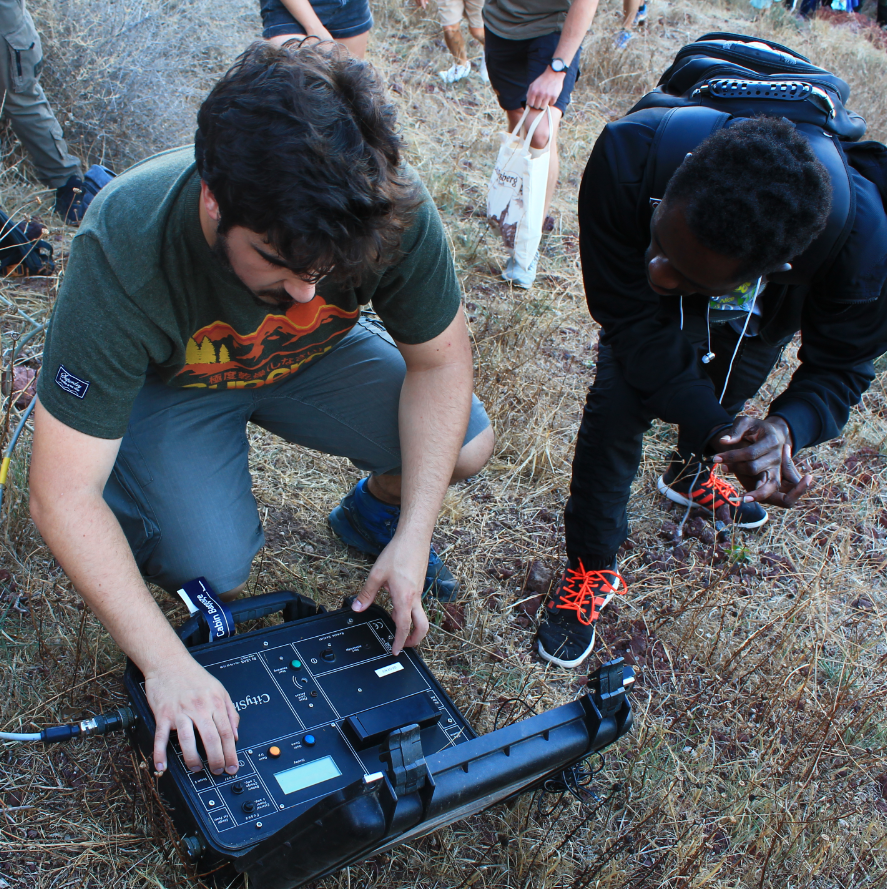
AMBIENT NOISE
Ambient noise measurement is a widely used geophysical technique to assess subsurface properties by analyzing naturally occurring seismic vibrations. This passive method relies on background seismic waves generated by natural or human activities, making it an efficient and non-invasive approach for site characterization. The horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio (H/V) method, in particular, is commonly used to estimate the resonance frequency of the ground, which provides insight into subsurface layering and soil properties.
In Santorini, we conducted H/V ambient noise measurements using a 1 Hz Lennartz 3-component sensor, connected to a Cityshark seismic station. The recordings, captured over 20 minutes, had a sampling rate of 200 Hz (with a 0.005 s sample interval). These data were then processed in the frequency domain to compute the horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratios, which allow for the identification of the ground's fundamental resonance frequency. This resonance frequency can provide valuable information for estimating the thickness of the upper soft soil layer.

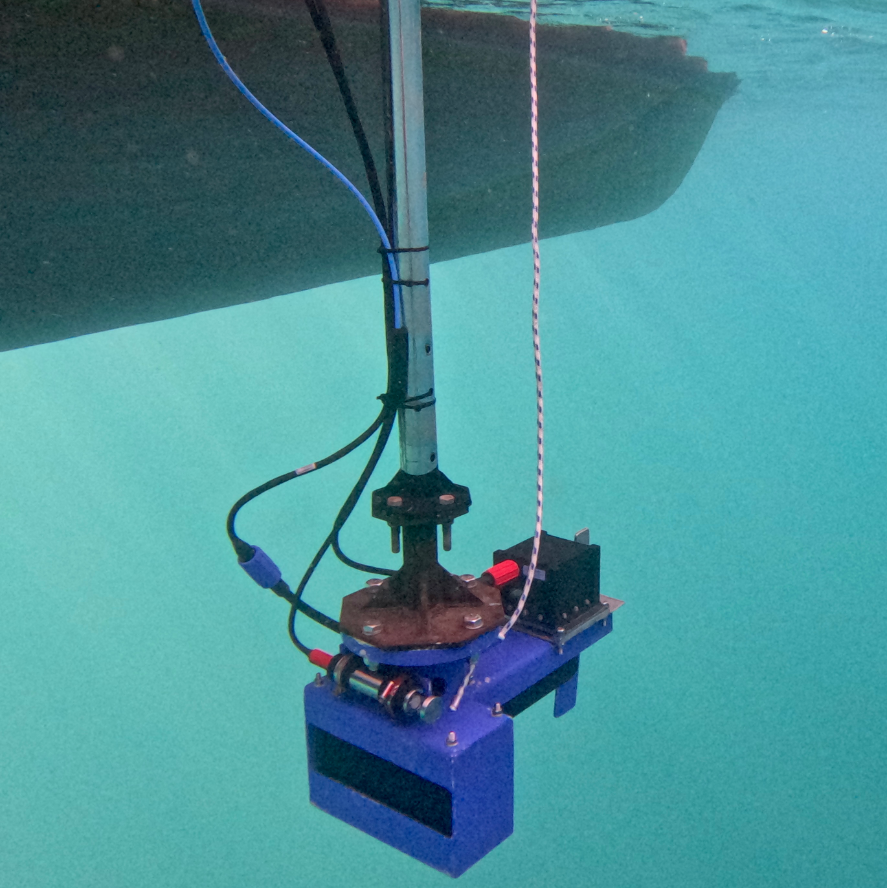
MULTIBEAM ECHOSOUNDER
The R2Sonic 2022 is a high-performance Multibeam Echosounder (MBES) designed for precise underwater mapping and surveying. Utilizing advanced sonar technology, it generates highly detailed 3D models of the seafloor. Its variable swath width capability allows users to adjust beam angles, optimizing coverage based on survey needs. Additional advanced features include real-time water column imaging, automated data processing, integrated data quality control tools, and an optional multispectral mode for enhanced analysis. Built with a rugged, compact design, the R2Sonic 2022 is ideal for deployment across various vessels and survey operations.
We originally planned to use this equipment during the summer school; however, due to unfavorable weather conditions, we were unable to conduct the survey. Despite this, students were introduced to the system, and a “dry installation” was simulated during the laboratory session. To ensure a hands-on learning experience, we provided students with a high-quality multibeam dataset acquired offshore Santorini's Red Beach during a previous project led by NKUA. This dataset was used during the lab session for data processing, enabling students to generate a submarine geospatial dataset suitable for integration with drone data collected offshore.
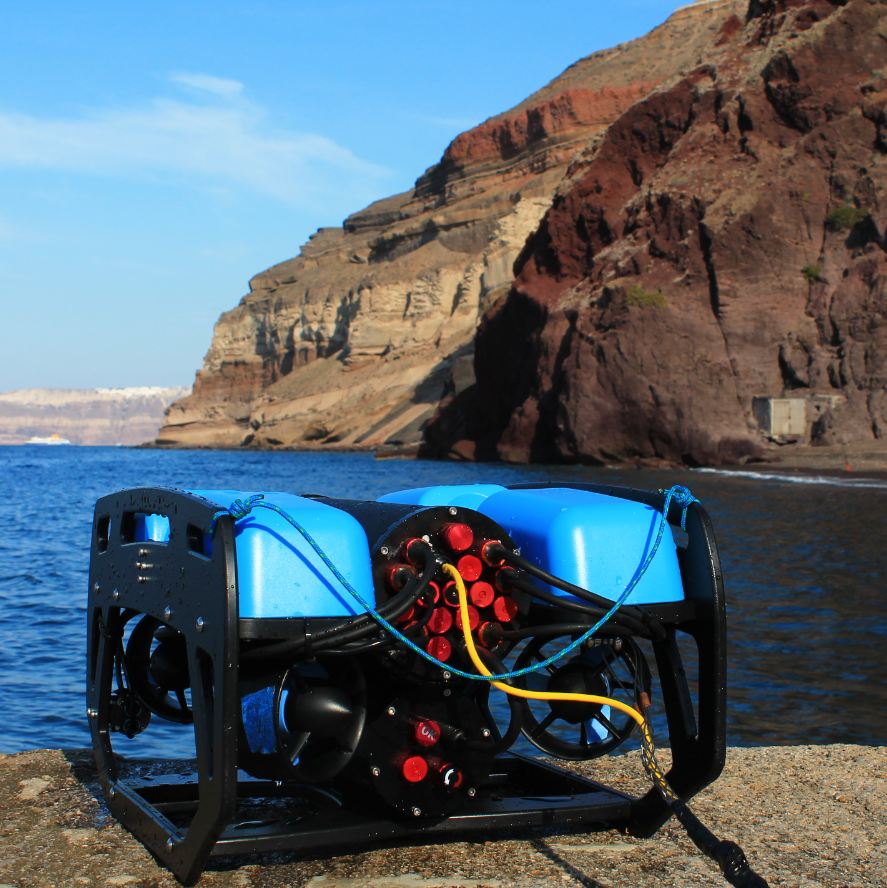
REMOTELY OPERATED VEHICLE
The future of ocean research and exploration is increasingly driven by robotics, with Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) playing a crucial role. ROVs are uncrewed, tethered underwater robots controlled by operators from a surface vessel. Equipped with high-definition cameras, robotic arms, and advanced sensors, they enable scientists to explore depths and environments that are otherwise inaccessible to humans. They offer real-time control and intervention, making them ideal for deep-sea research and environmental monitoring. Their ability to operate continuously and with precision makes them indispensable tools for modern ocean exploration.
The BlueROV2 used during the Summer School is a highly maneuverable, stable, and versatile observational ROV. Designed for operations in shallow to moderate waters, it features six thrusters, a rugged frame, and quick-swappable batteries, making it well-suited for extended underwater exploration. During field activities, students explored the offshore waters of Kokkinopetra Beach, gaining hands-on experience in remotely operated underwater surveys. The NKUA has been actively conducting research and surveys across Santorini’s offshore waters as part of numerous national and international projects, further contributing to marine exploration and scientific advancements.
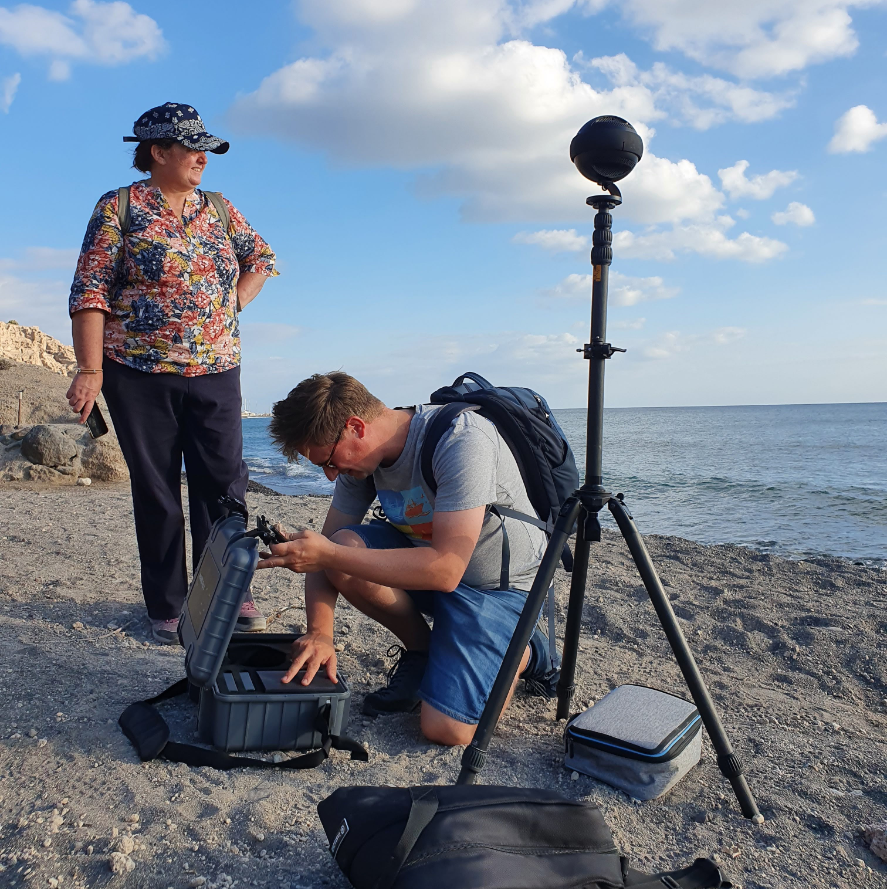


360° CAMERA
360° cameras are advanced tools that capture fully immersive imagery, allowing users to explore scenes from any angle. Using multiple ultra-wide lenses, they record spherical videos and photos, which are seamlessly stitched together for applications in VR experiences, virtual tours, education, and geospatial mapping. So far, this technology is most often used by real estate companies, the e-commerce sector and by GoogleStreetView for geospatial data. The opportunities for using 360° imagery for teaching in a virtual reality framework are endless and are evolving constantly. Indeed, they are becoming widely used in several fields, such as scientific research and environmental monitoring, offering new ways to document and interact with real-world environments.
During the Summer School, we utilized the Insta360 Pro 2, a professional-grade 360° camera equipped with six 4K lenses, capable of producing high-resolution 8K 360° footage. This cutting-edge technology enabled us to shoot videos and photos of the investigated research areas, and will allow us to create virtual tours contributing to deliverables such as a “virtual cruise” and an immersive guide for seamless land-to-sea geological modeling.

